The area of interest in the Atlantic, 90L, has become more likely to enter the Gulf of Mexico. After a time yesterday when it was trying to spin up, the system has stayed weak and is now beginning to encounter land. This land interaction will keep 90L weak as it passes through the Caribbean, making it even more likely to avoid the weakness in the Bermuda High that will be created by a trough. 90L currently has an area of moderate 700 mb to 850 mb vorticity associated with its convection. This area of vorticity is what currently passes for a circulation.
It is important to note that, even though the current state of the system is less organized than yesterday and the National Hurricane Center has lowered its percentage of becoming a tropical cyclone in the next 48 hours (which I would completely agree with), 90L has gained additional model support for its long-term development prospects. The cyclone-specific HWRF model was on board with 90L yesterday, taking it just south of Cuba and bringing it to 60 mph by the time it passes by. Today the HWRF keeps the system even farther south, intensifies 90L to a Category 1 hurricane, and sends it into the Yucatan. Additionally, the GFDL cyclone model, which was not doing anything at all with 90L yesterday, is today showing a Category 2 hurricane striking the Yucatan. I think that is overdoing it, personally, but this system is showing indications of going into the Gulf of Mexico and intensifying then.
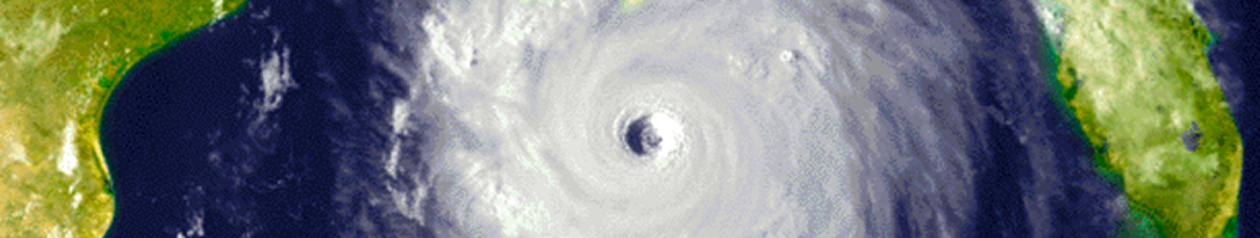
In recent hours, it has become possible that 90L is experiencing a center reformation. The center has been located in the part of the system that is now south of Puerto Rico. However, increased convection just south of Hispaniola (Fig. 1) is changing the polarity of the system, as is evident in upper-level divergence charts (Fig. 2). This convection is likely associated with the mountains and therefore does not indicate improvement in the tropical structure of 90L. However, if the center reforms to the northwest, this will throw a great deal of uncertainty into even the survival of 90L, as it will come much closer to the destructive mountains of Hispaniola and Cuba. If the reformation does not occur, we are looking at a track like that of the GFDL and HWRF. For my part, I am finding it hard to get on board with a center reformation over a more destructive environment that will make it hard for existing centers to stay together, let alone new ones to form, but time will tell.
One more important point to note for the GFDL model run is the strong ridge that would, in that scenario, serve to block 90L from moving north after it enters the Gulf. The blocking ridge does not extend that far west in the HWRF run, making a Central Gulf landfall possible.
In summary: 90L is in a state of transition at present, and the outcome of a number of possibilities will determine its fate. If the center reforms to the northwest, the GFDL and HWRF tracks should not be considered because they assume the present center. The result of a reformation would be more land interaction, which means a weak system, delays in development, and the possibility of complete dissipation. If the center does not reform, the GFDL and HWRF scenarios are in play, opening the doors for a significantly stronger system (and it should be noted that those models only go out to 126 hours, and have the system as an organized hurricane or near-hurricane in the middle of 90°F waters and low shear). The ultimate landfalling location of 90L will then depend on the strength and extent of the ridge.

Figure 1: Rainbow-enhanced infrared image of 90L, Saturday evening.

Figure 2: Upper-level divergence over 90L.