Not long ago, during spring break, I went to Huntsville, Alabama with family on a quick getaway. We’d had a harsh three weeks of winter conditions in an area that is unaccustomed to them, and which is certainly unaccustomed to four winter storms in about twenty days. We were also under assorted conditions of stress from work, school, and preparation for the future. We needed the trip, short though it would have to be.
No one in the car really wanted to drive on I-20/I-59. That stretch of interstate between Tuscaloosa and Birmingham is incredibly nerve-wracking and dangerous, and is not something I’d recommend to any driver unless one particularly savors the thrill of bumper-to-bumper 75 mph across three to four lanes and people passing with only feet to spare. We took the state highways instead. Some of the drive took place on Highway 43, a winding but generally pleasant stretch of road that passes through such Alabama towns as Hamilton and Hackleburg.
It was as we approached Hackleburg that we saw the first unusual scene: a swath of trees snapped, long denuded of leaves, bent down flush with the ground at assorted angles. The realization hit all of us at once.
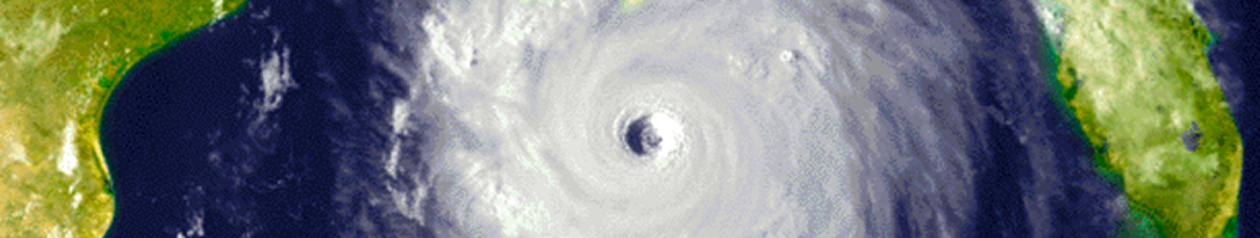
The track of the EF-5 “Hackleburg tornado” (really an extremely long-tracked tornado that began in far western Alabama and continued a little into Tennessee) paralleled Highway 43 early in its lifespan, and EF-5 damage was observed along this part of the path. The destruction we saw was not the organized logging of a timber company. They weren’t even the type of trees likely to be felled for commercial purposes.
It has been almost four years, and yet these downed trees still remain, a stark reminder of the violence of April 27, 2011.
We continued our drive. As we moved into Hackleburg, we saw the first one along the road. A heavy, inset, but otherwise unassuming rectangular door that opened into what appeared to be a small room built into a slope on the property.
“Storm cellar,” somebody remarked matter-of-factly, with no alteration of tone or pitch. It might have been me. I don’t recall who noticed the first one. We were all pointing them out before the end of it.
The “Hackleburg tornado” took 72 lives in rural and small-town Alabama, scouring 132 miles with its fury. The official survey claims that the winds were at least 210 mph. I am convinced that they were much higher than that in places.
We talked about things we remembered about this tornado. I was pretty sure that it had created a “situation” at the nuclear power plant in northern Alabama. It had.
“Storm cellar. Looks like the same kind as before.” And indeed the second one we noticed did look like the same design as the first one.
Although they are generally acceptable for shelter in most tornadoes, I am firmly of the opinion that basements and above-ground safe rooms (even reinforced) are insufficient to guarantee safety in EF-5 tornadoes. There have been basement fatalities before. I particularly recall that they happened in the 2008 Parkersburg, IA EF-5 tornado. Think about it: If a basement is even partially above surface level, or the flooring above it is not specially reinforced, then just what exactly is to prevent an EF-5 tornado (capable of leveling a house down to a bare slab foundation) from exposing a basement and then descending into it? If a safe room is above-ground, what is to prevent an EF-5 tornado (capable of hurling heavy metal tanks up to a mile, as happened in the 2013 Moore, OK tornado) from tossing a massive object right at it and crushing it?
“There’s another storm cellar.” Again the same type. Most likely the same contractor installed them.
I have some misgivings about the notion of building earthen walls around prefabricated storm shelters, particularly those plastic rooms that Southeasterners frequently saw advertised after the 2011 tornadoes. The tornado that I drove away from that day, the EF-5 Kemper/Neshoba tornado, dug trenches into the ground 2 feet deep. The storm shelters that we saw along Highway 43, however, appeared to have been built into natural embankments. I hope they are sufficiently deep into the ground that they could not likely be exposed by another monster of that sort.
“Another storm cellar.”
We were all pleased to see the residents of Hackleburg being prepared. It must have been an unimaginably traumatic event. I didn’t even lose anything, but merely the fear/expectation that I was going to lose everything left me with a mild case of PTSD-like symptoms every time the anniversary approached. In order to be sure of this, I would have to make the drive again with someone marking placing markers on a GPS-enabled map whenever we passed a house with a shelter, but it is even possible that these were all people who lost their homes in the 2011 tornado. They were certainly close to the EF-5 damage path, if not directly in it.
These appeared to be homes of middle-class residents. It should be easier for everyone to install a—
“Storm cellar.”
By then we were simply saying the words. It was almost like another road game, such as counting cars of a particular color. As we passed through Hackleburg proper, we couldn’t help but observe how much construction appeared to be quite new. Even the road had a new stretch of pavement, identifiable because of its smoother surface and different, darker color from the surrounding road. The tornado did tear up the asphalt as well. Intense tornadoes often do that.
“Storm cellar.”
If this stretch of road is representative of the community, that says something very positive about the residents of this area. I don’t support unfunded mandates to require private homeowners to have basements or storm shelters, because I think people should have the right to face private, personal risk as they see fit (after all, I did precisely that by choosing to hit the road to evade an EF-5 tornado, against the recommendation of the National Weather Service), but I am very glad when people do take the initiative to protect themselves and their families in this manner. I am in favor of the “carrot” of permanent tax credits for any expenditure of this nature.
There were six homes with the same kind of earthen, in-ground storm cellar just along Highway 43 between Hamilton and Hackleburg. I’ve never seen that many in such a small area before. It might not even be noticed by most people, especially people who did not know that an exceptionally violent tornado had occurred in this place four years earlier. But those of us who did have that bit of knowledge, and who still look at things outside the vehicle instead of some sort of onboard entertainment, noticed this series of doors opening to rooms in the ground. It was a subtle indicator of something different about this area.
Trauma changes people. What we saw that day, March 11, 2015, was proof positive that it changes communities too.